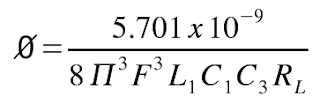Circuit diagram
I use the lm10 IC because it has a reference voltage and that is
useful for dc power supply. With two ICs can take different output
voltage and amperage. This circuit is protected from short circuit.P2 is
for controlling the current at the range of 0-2A. Stabilize the output
voltage with R4 on negative pin on op-amp and with R2 & P1 on
positive pin.
Op-amp output controls T1 that not let ripple of voltage.T1 increase
or decrease ampere of R6 and control the voltage of T5 & T4. Pin 1
is the reference voltage and reference voltage is losing some voltage on
R1 that has 100uA . This current passes through P1 too.
Vlose p1=100uA*Rp1
This lose voltage regulate output voltage rate of output current is
compare between reference voltage of P3 and lose voltage on R11.T3 is
protecting short circuit with R11. For reduce out put voltage to 0v
should parallel one resistor 470 ohm in out put. Minimum voltage is
0.4v. The maximum output voltage is fixed with R1b and should not become
over of 50v. Therefore your transformer should give 36V, 3A with 4700uF
capacitor. T6, T5, T7 need heatsilk.
R1a = 2,2 K
R1b = read the text
R2 = 10 K
R3, R7 = 3.3 k
R4 = 390 Ohm
R5 = 47 K
R6 = 3.3 K 1Watt
R8 = 180 Ohm
R9, R10 = 0.47 Ohm 3Watt
R11 = 0.075 Ohm 2Watt
R12 = 470 Ohm
P1 = 500K liner potentiometer
P2 = 4.7 K potentiometer
P3 = 10 K potentiometer
C1 = 1nF
C2 = 10nF
C3 = 22nF
C4 = 47mF 63v electrolytic
C5 = 4700mF 80v electrolytic
T1, T2 = BC161
T3, T4 = BD141
T5 = BD241
T6, T7 = 2V3055
D1, D2 = 1N4148
D3, D4 = 1N4001
IC1, IC2 = LM10C
Author: hamed_iranmehr@yahoo.com
Showing posts with label power supply. Show all posts
Showing posts with label power supply. Show all posts
Sunday, July 29, 2012
Thursday, July 5, 2012
Variable DC Power Supply Circuit
Circuit diagram
Voltage range: 0.7 - 24V
Current limiting range: 50mA - 2A
Parts:
P1 500R Linear Potentiometer
P2 10K Log. Potentiometer
R1,R2 2K2 1/2W Resistors
R3 330R 1/4W Resistor
R4 150R 1/4W Resistor
R5 1R 5W Resistor
C1 3300�F 35V Electrolytic Capacitor (see Notes)
C2 1�F 63V Polyester Capacitor
D1,D2 1N5402 200V 3A Diodes
D3 5mm. Red LED
Q1 BC182 50V 100mA NPN Transistor
Q2 BD139 80V 1.5A NPN Transistor
Q3 BC212 50V 100mA PNP Transistor
Q4 2N3055 60V 15A NPN Transistor
T1 220V Primary, 36V Center-tapped Secondary 50VA Mains transformer (see Notes)
PL1 Male Mains plug
SW1 SPST Mains switch
Device purpose:
A Variable DC Power Supply is one of the most useful tools on the electronics hobbyist's workbench. This circuit is not an absolute novelty, but it's simple, reliable, "rugged" and short-proof, featuring variable voltage up to 24V and variable current limiting up to 2A. It's well suited to supply the circuits shown in this website. You can adapt it to your own requirements as explained in the notes below.
Notes:
P1 sets the maximum output current you want to be delivered by the power supply at a given output voltage.
P2 sets the output voltage and must be a logarithmic taper type, in order to obtain a more linear scale voltage indication.
You can choose the Transformer on the grounds of maximum voltage and current output needed.
Best choices are: 36, 40 or 48V center-tapped and 50, 75, 80 or 100VA.
Capacitor C1 can be 2200 to 6800�F, 35 to 50V.
Q4 must be mounted on a good heatsink in order to withstand sustained output short-circuit.
In some cases the rear panel of the metal box in which you will enclose the circuit can do the job.
The 2N3055 transistor (Q4) can be replaced with the slightly less powerful TIP3055 type.
Voltage range: 0.7 - 24V
Current limiting range: 50mA - 2A
Parts:
P1 500R Linear Potentiometer
P2 10K Log. Potentiometer
R1,R2 2K2 1/2W Resistors
R3 330R 1/4W Resistor
R4 150R 1/4W Resistor
R5 1R 5W Resistor
C1 3300�F 35V Electrolytic Capacitor (see Notes)
C2 1�F 63V Polyester Capacitor
D1,D2 1N5402 200V 3A Diodes
D3 5mm. Red LED
Q1 BC182 50V 100mA NPN Transistor
Q2 BD139 80V 1.5A NPN Transistor
Q3 BC212 50V 100mA PNP Transistor
Q4 2N3055 60V 15A NPN Transistor
T1 220V Primary, 36V Center-tapped Secondary 50VA Mains transformer (see Notes)
PL1 Male Mains plug
SW1 SPST Mains switch
Device purpose:
A Variable DC Power Supply is one of the most useful tools on the electronics hobbyist's workbench. This circuit is not an absolute novelty, but it's simple, reliable, "rugged" and short-proof, featuring variable voltage up to 24V and variable current limiting up to 2A. It's well suited to supply the circuits shown in this website. You can adapt it to your own requirements as explained in the notes below.
Notes:
P1 sets the maximum output current you want to be delivered by the power supply at a given output voltage.
P2 sets the output voltage and must be a logarithmic taper type, in order to obtain a more linear scale voltage indication.
You can choose the Transformer on the grounds of maximum voltage and current output needed.
Best choices are: 36, 40 or 48V center-tapped and 50, 75, 80 or 100VA.
Capacitor C1 can be 2200 to 6800�F, 35 to 50V.
Q4 must be mounted on a good heatsink in order to withstand sustained output short-circuit.
In some cases the rear panel of the metal box in which you will enclose the circuit can do the job.
The 2N3055 transistor (Q4) can be replaced with the slightly less powerful TIP3055 type.
Variable Power Supply Using Fixed Regulator
Description:
This is a similar power supply that I used to power my FM Transmitter. After suffering long problems with mains hum, this design using a pi filtered C-L-C approach. This circuit offers excellent ripple rejection.
Parts List:
T1 Transformer 10:1 Secondary 24V @ 2A
BR1 Bridge Rectifier 50V PIV 2A rating
C1 4700u (35V)
C2 0.001u
C3 2200u (35V)
C4 0.001u
C5 4.7u (25)
C6 0.01u
R1 10k potentiometer
L1 see text
U1 7805 N.B. This may be changed for different output voltages e.g. 7812 for higher output voltage
ZD1 15V zener @ 1.3W
Notes:
Looking at the above schematic, the specific inductance of the ferrite (core)is important. A core should be chosen to work within the specific frequency as stated by the manufacturer. L1 is a powder core and has 32 turns of 0.75mm wire.
The transformer has a 240V primary and has a secondary rated 24V at 2A. The bridge rectifier contains 4 diodes, their current rating needs to be high with respect to the transformers output current; if not the current may damage the diodes. I used MR751 which is rated 6 amps, but another good choice is 1N5400. C1 is the mainfiltering capacitor, the supply is further smoothed by the combination of L1 and C3. C2 and C4 are decoupling capacitors; their action further reduce ripple factor.
The regulator, U1 utilizes the action of zener diode ZD1 which is in parallel with the potentiometer, R1. The tuning action of R1 produces a variable regulator output. The output voltage is variable from the regulator output to the regulator output plus the zener voltage. E.G. A 7805 regulator and 10V zener give an output adjustable from 5 to 15 Volts. The regulator may be changed to provide different output voltages as may the zener. the zener should be rated a minimum of 1.3 Watts. All the parts should be available at local electronic shops.
Formula for calculating Ripple Factor in Filters:
Where:
Φ = Ripple Factor
F = frequency of supply in Hz
L = inductance of L1 in uH
C1 = capacitance of C1 in uF
C3 = capacitance of C3 in uF
RL = load resistance in ohms
Wednesday, July 4, 2012
Regulated 12 Volt Supply Circuit
Description
A basic regulated 12 Volt power supply
Circuit diagram
Notes:
This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0.7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12.3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit.
A basic regulated 12 Volt power supply
Circuit diagram
Notes:
This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0.7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12.3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Circuit diagram I use the lm10 IC because it has a reference voltage and that is useful for dc power supply. With two ICs can take d...
-
Circuit diagram How to calculate transformer rating The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power...
-
Low-cut and Bass controls Output power: 40W on 8 Ohm and 60W on 4 Ohm loads Amplifier circuit diagram: Amplifier parts: R1 6K8 ...
-
circuit diagram Parts: P1 22K Log.Potentiometer (Dual-gang for stereo) P2 100K Log.Potentiometer (Dual-gang for stereo) R1 820...